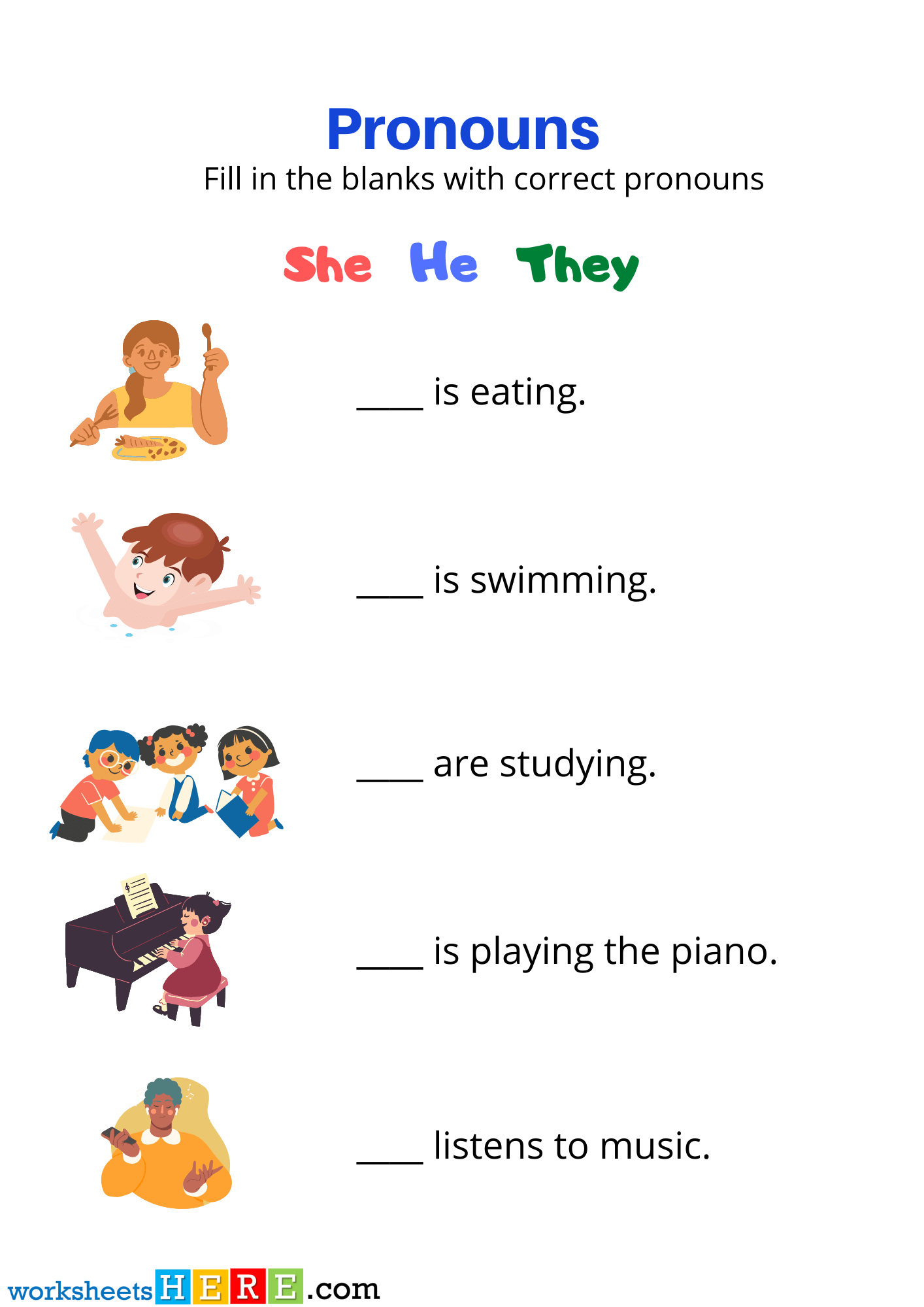
Personal Pronouns and Possessive Adjectives with Pictures PDF Worksheet For Kids
For Download PDF Worksheet, Click Here; Personal Pronouns and Possessive Adjectives with Pictures PDF Worksheet For Kids
Object Pronouns
Pronouns are noun words that can be used in place of the names of entities in a sentence and can fulfill all the functions that nouns do. Object pronouns are pronouns that replace the object noun in a sentence.
The pronouns mentioned are “I, me” for the first person singular, “you” for the second person singular, and “he, she, it, him, her” for the third person singular. “we” and “us” are used for the first person plural, “you” is used again for the second person plural, and “they” and “them” are used for the third person plural. If we need to show them through a table, we can use a table like the one below.
For Download PDF Worksheet, Click Here; Subject Object Pronouns and Possessive Adjectives Chart PDF Worksheet For Students
| Subject | Object |
| I | Me |
| You | You |
| He | Him |
| She | Her |
| It | It |
| We | Us |
| You | You |
| They | Them |
Subject Pronouns
The situation is considerably more perplexing in English because many cases have vanished. There are seven examples in modern Ukrainian. There are fifteen examples in Finnish. Even German, which belongs to the same linguistic family as English, has four. There are three in English, which is about as straightforward as it gets linguistically. Because most native speakers are expected to have an intuitive “feel” for the right case usage, English cases are rarely taught nowadays.
Many people, however, continue to make mistakes, and the lack of educational reinforcement just adds to the uncertainty. The focus of this article will be on two cases: subject (nominative) and object, with a special emphasis on first-person pronouns. Read on if you’ve ever been puzzled about the terms “I versus. me,” “he vs. him,” “she vs. her,” “we vs. us,” or “they vs. them.”
- I have got a motorbike.
- You are not very tall.
- My lovely sister is playing American flag football.
- She is coming tomorrow night.
- It is snowy and windy.
- We went to the cinema.
Possessive Adjectives
Possessive adjectives express the belonging of an object or thing. Unlike possessive pronouns, which replace nouns, possessive adjectives precede nouns to replace them. Possessive adjectives can help organize sentences, just like independent possessive pronouns. To understand what is being said here, let’s first look at a sentence that does not contain possessive adjectives and sounds a bit cumbersome:
Bill loves Bill’s car.
It seems odd to use the name Bill twice in this sentence. A possessive adjective that we will use here eliminates the problem.
Bill loves his car very much.